SSH Agent
STDIOMCP server for SSH connection management and remote command execution
MCP server for SSH connection management and remote command execution
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) server for managing and controlling SSH connections. This server integrates seamlessly with Claude Desktop and other MCP-compatible clients to provide AI-powered SSH operations.
This MCP server provides SSH operations through a clean, standardized interface that can be used by MCP-compatible language models like Claude Desktop. The server automatically discovers SSH hosts from your ~/.ssh/config and ~/.ssh/known_hosts files and executes commands using native SSH tools for maximum reliability.
The easiest way to install MCP SSH Agent is through the Desktop Extension (.dxt) format:
mcp-ssh-*.dxt file from the GitHub releases page.dxt file to install it in Claude Desktopnpx @aiondadotcom/mcp-ssh
To use this MCP server with Claude Desktop using manual configuration, add the following to your MCP settings file:
On macOS: ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
On Windows: %APPDATA%/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
{ "mcpServers": { "mcp-ssh": { "command": "npx", "args": ["@aiondadotcom/mcp-ssh"] } } }
After adding this configuration, restart Claude Desktop. The SSH tools will be available for use in your conversations with Claude.
npm install -g @aiondadotcom/mcp-ssh
git clone https://github.com/aiondadotcom/mcp-ssh.git cd mcp-ssh npm install npm start
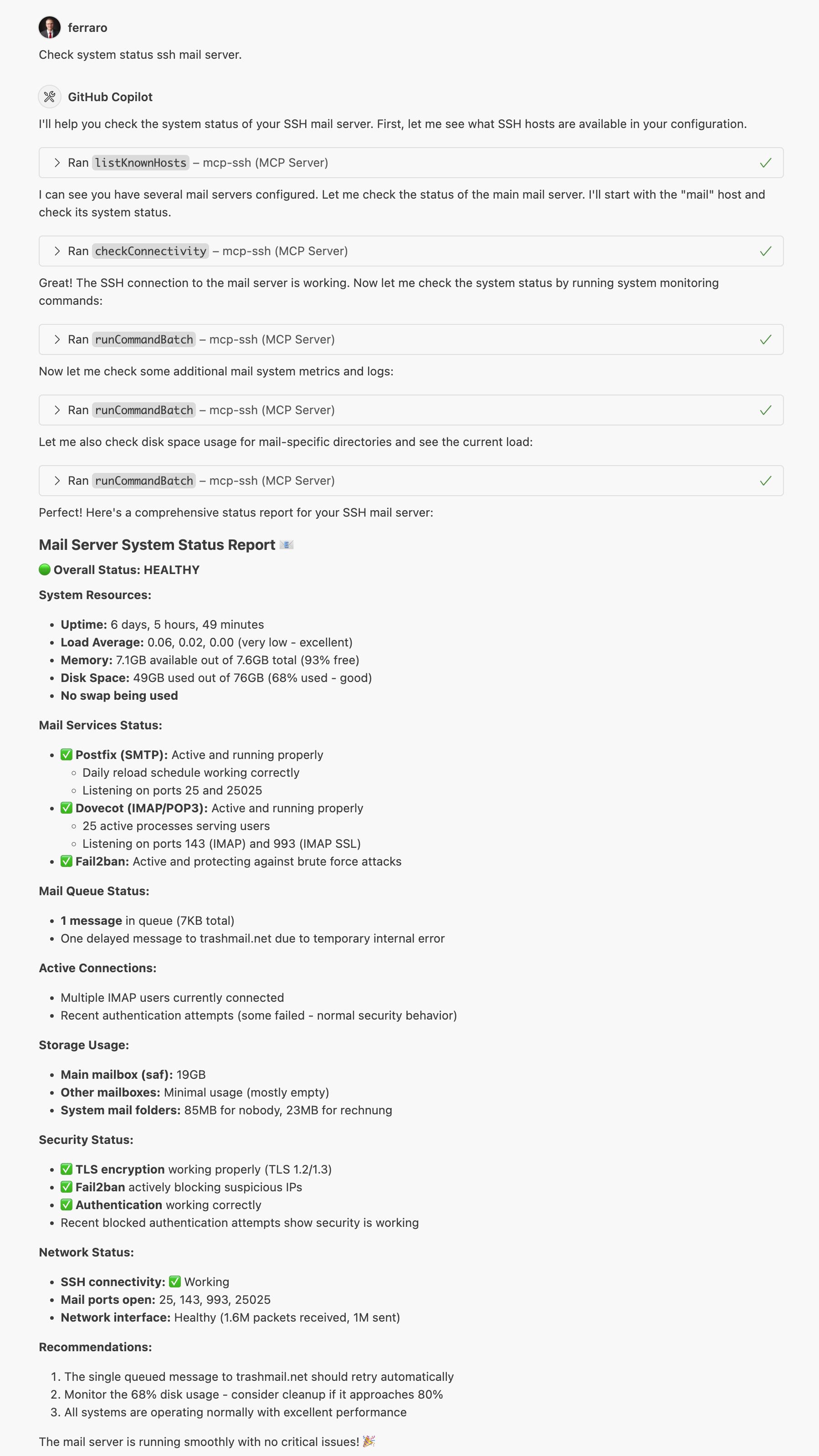
The screenshot above shows the MCP SSH Agent in action, demonstrating how it integrates with MCP-compatible clients to provide seamless SSH operations.
This screenshot demonstrates the MCP SSH Agent integrated with Claude, showing how the AI assistant can directly manage SSH connections and execute remote commands through the MCP protocol.
ssh/scp commands instead of JavaScript SSH librariesscpThe agent provides the following MCP tools:
sshscpscpHere's how your Claude Desktop configuration should look:
{ "mcpServers": { "mcp-ssh": { "command": "npx", "args": ["@aiondadotcom/mcp-ssh"] } } }
If you prefer to run the server manually or integrate it with other MCP clients:
{ "servers": { "mcp-ssh": { "command": "npx", "args": ["@aiondadotcom/mcp-ssh"] } } }
ssh and scp commands available)~/.ssh/config and ~/.ssh/known_hosts)Once configured, you can ask Claude to help you with SSH operations like:
Claude will use the MCP SSH tools to perform these operations safely and efficiently.
The agent runs as a Model Context Protocol server over STDIO. When installed via npm, you can use it directly:
# Run via npx (recommended) npx @aiondadotcom/mcp-ssh # Or if installed globally mcp-ssh # For development - run with debug output npm start
The server communicates via clean JSON over STDIO, making it perfect for MCP clients like Claude Desktop.
MCP_SILENT=true - Disable debug output (automatically set when used as MCP server)The agent reads from standard SSH configuration files:
~/.ssh/config - SSH client configuration (supports Include directives)~/.ssh/known_hosts - Known host keysMake sure your SSH keys are properly configured and accessible via SSH agent or key files.
The MCP SSH Agent fully supports SSH Include directives to organize your configuration across multiple files. However, there's an important SSH bug to be aware of:
⚠️ SSH Include Directive Bug Warning
SSH has a configuration parsing bug where Include statements must be placed at the beginning of your ~/.ssh/config file to work correctly. If placed at the end, SSH will read them but won't properly apply the included configurations.
✅ Correct placement (at the beginning):
# ~/.ssh/config Include ~/.ssh/config.d/* Include ~/.ssh/work-hosts # Global settings ServerAliveInterval 55 # Host definitions Host myserver HostName example.com
❌ Incorrect placement (at the end) - won't work:
# ~/.ssh/config # Global settings ServerAliveInterval 55 # Host definitions Host myserver HostName example.com # These Include statements won't work properly due to SSH bug: Include ~/.ssh/config.d/* Include ~/.ssh/work-hosts
The MCP SSH Agent correctly processes Include directives regardless of their placement in the file, so you'll get full host discovery even if SSH itself has issues with your configuration.
Here's an example SSH configuration file that demonstrates various connection scenarios including Include directives:
# Include directives must be at the beginning due to SSH bug Include ~/.ssh/config.d/* Include ~/.ssh/work-servers # Global settings - keep connections alive ServerAliveInterval 55 # Production server with jump host Host prod Hostname 203.0.113.10 Port 22022 User deploy IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_prod_rsa # Root access to production (separate entry) Host root@prod Hostname 203.0.113.10 Port 22022 User root IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_prod_rsa # Archive server accessed through production jump host Host archive Hostname 2001:db8:1f0:cafe::1 Port 22077 User archive-user ProxyJump prod # Web servers with specific configurations Host web1.example.com Hostname 198.51.100.15 Port 22022 User root IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 Host web2.example.com Hostname 198.51.100.25 Port 22022 User root IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 # Database server with custom key Host database Hostname 203.0.113.50 Port 22077 User dbadmin IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_database_rsa IdentitiesOnly yes # Mail servers Host mail1 Hostname 198.51.100.88 Port 22078 User mailuser Host root@mail1 Hostname 198.51.100.88 Port 22078 User root # Monitoring server Host monitor Hostname 203.0.113.100 Port 22077 User monitoring IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_monitor_ed25519 IdentitiesOnly yes # Load balancers Host lb-a Hostname 198.51.100.200 Port 22077 User root Host lb-b Hostname 198.51.100.201 Port 22077 User root
This configuration demonstrates:
ServerAliveInterval to keep connections aliveprod and root@prod)ProxyJump to access servers through bastion hostsIdentitiesOnly yes to use only specified keysThe MCP SSH agent automatically discovers and uses your SSH configuration:
~/.ssh/config are automatically availablessh command, so all config options workExample Usage with Claude Desktop:
prod, archive, web1.example.com, etc.ssh and scp are installed and in your PATH~/.ssh/config or ~/.ssh/known_hostsRun with debug output to see detailed operation logs:
# Enable debug mode MCP_SILENT=false npx @aiondadotcom/mcp-ssh
For the MCP SSH Agent to work properly, you need to set up SSH key authentication. Here's a complete guide:
Generate a new SSH key pair (use Ed25519 for better security):
# Generate Ed25519 key (recommended) ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "[email protected]" # Or generate RSA key (if Ed25519 is not supported) ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "[email protected]"
Important: When prompted for a passphrase, leave it empty (press Enter). The MCP SSH Agent cannot handle password-protected keys as it runs non-interactively.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Press Enter]
Enter same passphrase again: [Press Enter]
This creates two files:
~/.ssh/id_ed25519 (private key) - Keep this secret!~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub (public key) - This gets copied to serversCopy your public key to the remote server's authorized_keys file:
# Method 1: Using ssh-copy-id (easiest) ssh-copy-id user@hostname # Method 2: Manual copy cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub | ssh user@hostname "mkdir -p ~/.ssh && cat >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys" # Method 3: Copy and paste manually cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub # Then SSH to the server and paste into ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
To enable secure key-only authentication on your SSH servers, edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config:
# Edit SSH daemon configuration sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Add or modify these settings:
# Enable public key authentication PubkeyAuthentication yes AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys # Disable password authentication (security best practice) PasswordAuthentication no ChallengeResponseAuthentication no UsePAM no # Root login options (choose one): # Option 1: Allow root login with SSH keys only (recommended for admin access) PermitRootLogin prohibit-password # Option 2: Completely disable root login (most secure, but less flexible) # PermitRootLogin no # Optional: Restrict SSH to specific users AllowUsers deploy root admin # Optional: Change default port for security Port 22022
After editing, restart the SSH service:
# On Ubuntu/Debian sudo systemctl restart ssh # On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora sudo systemctl restart sshd # On macOS sudo launchctl unload /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/ssh.plist sudo launchctl load /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/ssh.plist
SSH is very strict about file permissions. Set them correctly:
On your local machine:
chmod 700 ~/.ssh chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 chmod 644 ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub chmod 644 ~/.ssh/config chmod 644 ~/.ssh/known_hosts
On the remote server:
chmod 700 ~/.ssh chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Test your connection before using with MCP SSH Agent:
# Test connection ssh -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 user@hostname # Test with verbose output for debugging ssh -v -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 user@hostname # Test specific configuration ssh -F ~/.ssh/config hostname
You can create different keys for different servers:
# Create specific keys ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f ~/.ssh/id_production -C "production-server" ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f ~/.ssh/id_staging -C "staging-server"
Then configure them in ~/.ssh/config:
Host production Hostname prod.example.com User deploy IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_production IdentitiesOnly yes Host staging Hostname staging.example.com User deploy IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_staging IdentitiesOnly yes
AllowUsersPermitRootLogin prohibit-password - Allows root access with SSH keys only (recommended for admin tasks)PermitRootLogin no - Completely disables root login (most secure, but requires sudo access)For developers who want to build DXT packages locally:
# Install dependencies npm install # Build the DXT package npm run build:dxt
This creates a .dxt file in the build/ directory that can be installed in Claude Desktop.
To publish a new DXT release:
# Build the DXT package npm run build:dxt # Create a GitHub release with the DXT file gh release create v1.0.3 build/mcp-ssh-1.0.3.dxt --title "Release v1.0.3" --notes "MCP SSH Agent v1.0.3"
The DXT file will be available as a release asset for users to download and install.
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
MIT License - see LICENSE file for details.
mcp-ssh/
├── server-simple.mjs # Main MCP server implementation
├── manifest.json # DXT package manifest
├── package.json # Dependencies and scripts
├── README.md # Documentation
├── LICENSE # MIT License
├── CHANGELOG.md # Release history
├── PUBLISHING.md # Publishing instructions
├── start.sh # Development startup script
├── start-silent.sh # Silent startup script
├── scripts/
│ └── build-dxt.sh # DXT package build script
├── doc/
│ ├── example.png # Usage example screenshot
│ └── Claude.png # Claude Desktop integration example
├── src/ # TypeScript source files (development)
│ ├── ssh-client.ts # SSH operations implementation
│ ├── ssh-config-parser.ts # SSH configuration parsing
│ └── types.ts # Type definitions
└── tsconfig.json # TypeScript configuration
This project is maintained by aionda.com and provides a reliable bridge between AI assistants and SSH infrastructure through the Model Context Protocol.