Emacs
STDIOMCP server connecting LLMs directly to Emacs for buffer manipulation and elisp execution
MCP server connecting LLMs directly to Emacs for buffer manipulation and elisp execution
Connect Large Language Models directly to your Emacs environment! This MCP (Model Context Protocol) server exposes Emacs functionality through standardized tools, allowing LLMs like Claude to read and modify your buffers, execute elisp code, navigate files, and much more.
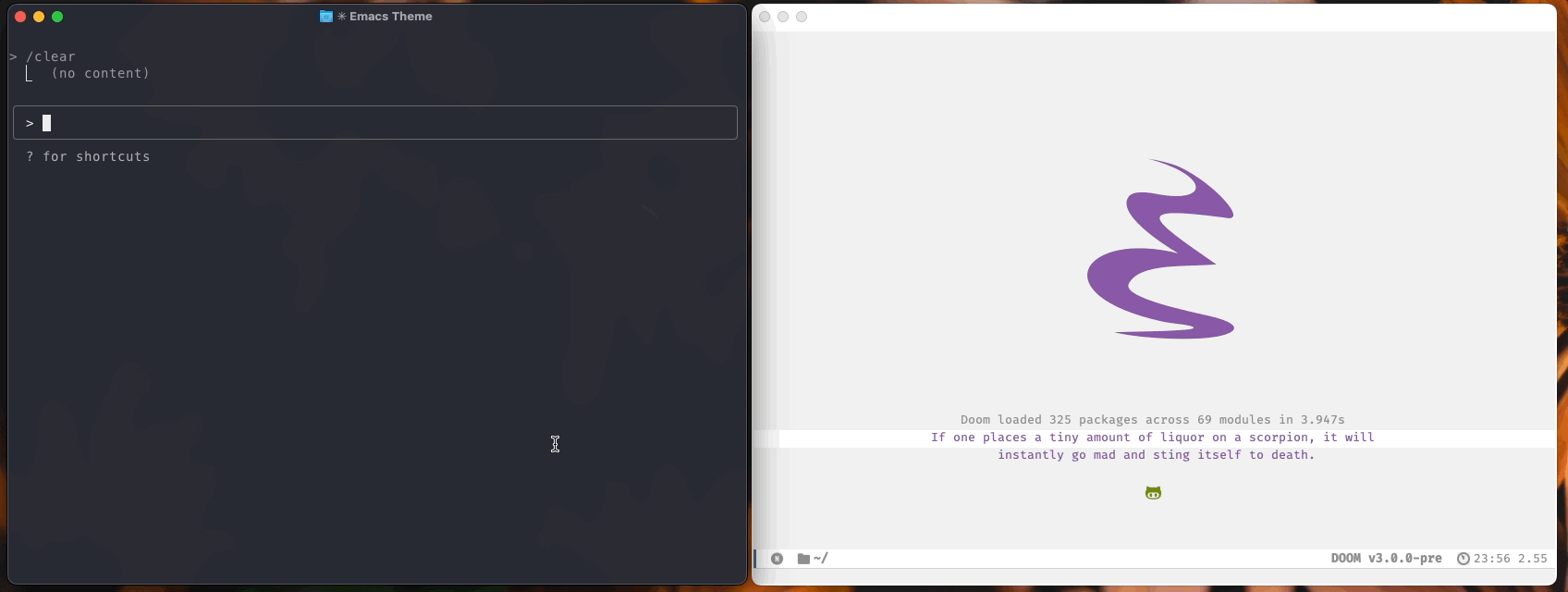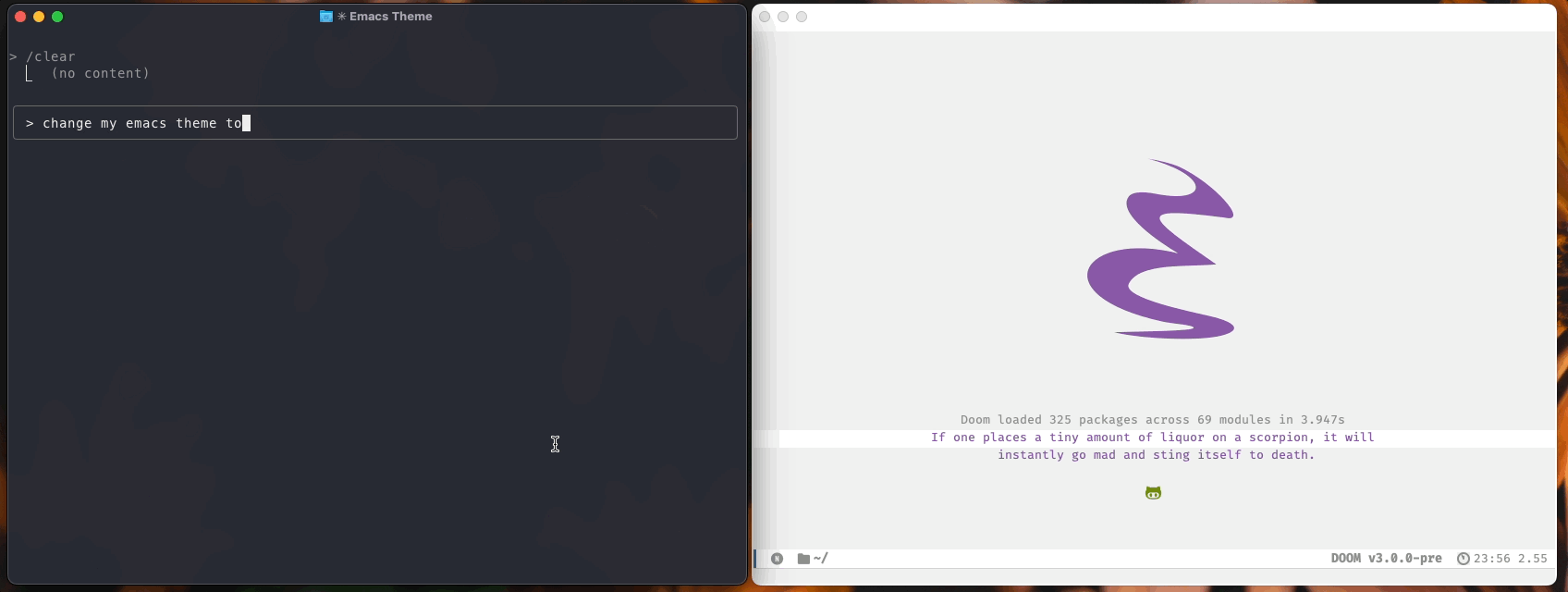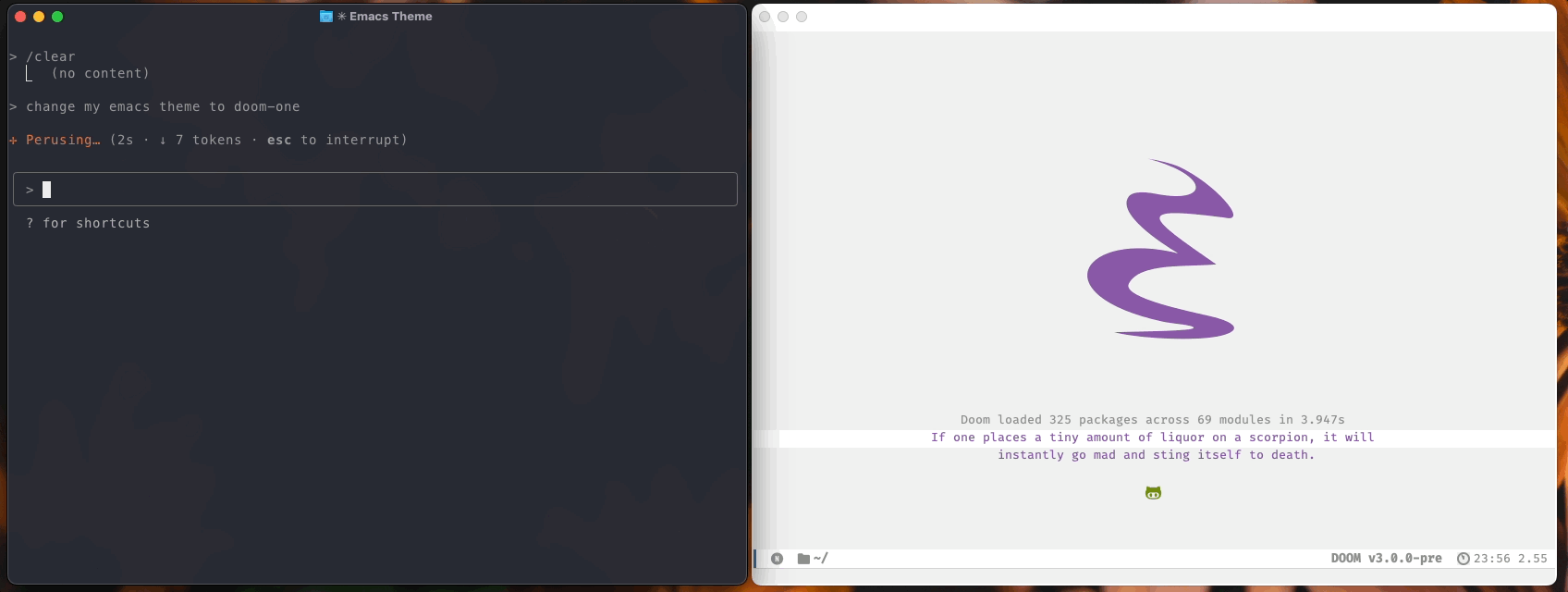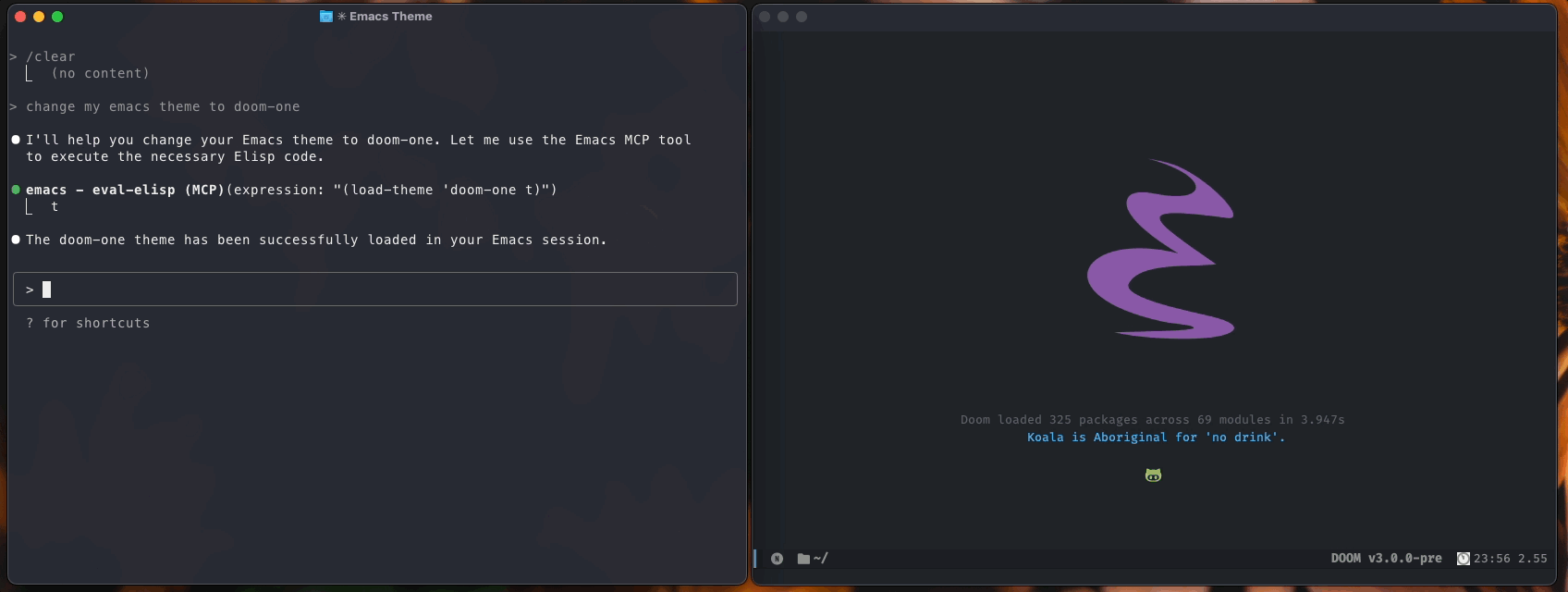
Installation: Place the files in your Emacs configuration directory and add to your config:
(add-to-list 'load-path "~/path-to/mcp-server") (require 'mcp-server)
Alternatively, use package managers:
;; Using straight.el (use-package mcp-server :straight (:type git :host github :repo "rhblind/emacs-mcp-server" :files ("*.el" "mcp-wrapper.py" "mcp-wrapper.sh")) :config (add-hook 'emacs-startup-hook #'mcp-server-start-unix)) ;; Using use-package with manual path (use-package mcp-server :load-path "~/path-to/mcp-server" :config (add-hook 'emacs-startup-hook #'mcp-server-start-unix)) ;; Using Doom Emacs package! macro (package! mcp-server :recipe (:type git :host github :repo "rhblind/emacs-mcp-server" :files ("*.el" "mcp-wrapper.py" "mcp-wrapper.sh")))
Start the server: Run M-x mcp-server-start-unix in Emacs. The server creates a Unix socket at ~/.config/emacs/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock (or similar based on your Emacs configuration).
Connect Claude Desktop: Add this to your Claude Desktop configuration:
[!NOTE] Make sure you have
socatinstalled!
{ "mcpServers": { "emacs": { "command": "socat", "args": ["-", "UNIX-CONNECT:~/.config/emacs/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock"], "transport": "stdio" } } }
Connect Claude CLI
claude mcp add emacs ~/path-to/mcp-wrapper.py ~/.config/emacs/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock # Uses the python script claude mcp add emacs ~/path-to/mcp-wrapper.sh ~/.config/emacs/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock # Uses the bash script claude mcp add emacs-direct -- socat - UNIX-CONNECT:$HOME/.config/emacs/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock # Uses socat directly # Real world, add to user scope so it's always available claude mcp add emacs --scope user ~/.config/emacs/.local/straight/build-30.1/mcp-server/mcp-wrapper.py ~/.config/emacs/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock
That's it! Claude can now interact with your Emacs session.
Once connected, LLMs can perform powerful operations in your Emacs environment:
Code and Text Manipulation
Emacs Integration
M-x command programmaticallyExample Interactions:
Current Tool:
eval-elisp - Execute arbitrary elisp expressions safely and return the resultWhat you can do now: With the eval-elisp tool, you can already accomplish a lot! LLMs can:
(buffer-string) or (with-current-buffer "filename.txt" (buffer-string))(insert "text") or (with-current-buffer "filename.txt" (insert "text"))(find-file "path/to/file") or (switch-to-buffer "buffer-name")(point) or (line-number-at-pos)(goto-char 100) or (goto-line 50)(if (region-active-p) (buffer-substring (region-beginning) (region-end)) "No selection")(mapcar #'buffer-name (buffer-list))(call-interactively 'command-name) or (command-name)variable-name or (setq variable-name value)Planned tools for future implementation include dedicated functions for buffer management (get-buffer-content, set-buffer-content, get-buffer-list), navigation (get-point, goto-point, insert-at-point), variable access (get-variable, set-variable), and window operations (get-window-configuration).
Socket naming strategies: Choose how sockets are named based on your setup:
(setq mcp-server-socket-name nil) ; Default: emacs-mcp-server.sock (setq mcp-server-socket-name 'user) ; User-based: emacs-mcp-server-{username}.sock (setq mcp-server-socket-name 'session) ; Session-based: emacs-mcp-server-{username}-{pid}.sock (setq mcp-server-socket-name "custom") ; Custom: emacs-mcp-server-custom.sock
Other configuration options:
;; Custom socket directory (setq mcp-server-socket-directory "~/.config/emacs-mcp/") ;; Auto-start server when Emacs starts (add-hook 'emacs-startup-hook #'mcp-server-start-unix) ;; Enable debug logging (setq mcp-server-debug t)
The MCP server implements comprehensive security measures to protect your Emacs environment and sensitive data from unauthorized access by LLMs.
Permission System:
delete-file, shell-command, find-file require user approval.authinfo, .netrc, SSH keys, etc.)*Messages*, *shell*, *terminal*Input Validation:
Execution Limits:
The server automatically protects these sensitive file patterns:
Authentication Files:
~/.authinfo* - Emacs authentication data~/.netrc* - Network authentication credentials~/.ssh/ - SSH keys and configuration~/.gnupg/ - GPG keys and configurationCloud & Service Credentials:
~/.aws/ - AWS credentials~/.docker/config.json - Docker authentication~/.kube/config - Kubernetes configuration~/.config/gh/ - GitHub CLI credentialsSystem Files:
/etc/passwd, /etc/shadow - System authentication~/.password-store/ - Password manager dataUsers have complete control over the security model through customizable settings:
Customize Sensitive Files:
;; Add your own sensitive file patterns (setq mcp-server-security-sensitive-file-patterns '("~/.authinfo" "~/.ssh/" "~/my-secrets/" "*.key")) ;; Allow specific sensitive files without prompting (setq mcp-server-security-allowed-sensitive-files '("~/.authinfo" "~/safe-config.txt"))
Customize Dangerous Functions:
;; Modify which functions require permission (setq mcp-server-security-dangerous-functions '(delete-file shell-command find-file write-region)) ;; Allow specific functions without prompting (setq mcp-server-security-allowed-dangerous-functions '(find-file dired)) ; Allow file browsing freely
Global Security Settings:
;; Disable all permission prompts (not recommended) (setq mcp-server-security-prompt-for-permissions nil) ;; Customize execution timeout (setq mcp-server-security--max-execution-time 60) ; 60 seconds ;; Add custom sensitive buffer patterns (setq mcp-server-security-sensitive-buffer-patterns '("*Messages*" "*shell*" "*my-secure-buffer*"))
Use Emacs Customize Interface:
M-x customize-group RET mcp-server RET
Paranoid Mode (Maximum Security):
;; Very restrictive - prompts for everything (setq mcp-server-security-dangerous-functions '(find-file insert-file-contents switch-to-buffer eval load require)) (setq mcp-server-security-allowed-dangerous-functions nil) (setq mcp-server-security-prompt-for-permissions t)
Permissive Mode (Development):
;; More relaxed for trusted development scenarios (setq mcp-server-security-allowed-dangerous-functions '(find-file dired switch-to-buffer insert-file-contents)) ;; Keep file protections for credentials (setq mcp-server-security-sensitive-file-patterns '("~/.authinfo*" "~/.netrc*" "~/.ssh/" "~/.gnupg/"))
Whitelist-Only Mode (Ultra Secure):
;; Only allow explicitly whitelisted operations (setq mcp-server-security-prompt-for-permissions nil) ; No prompts - just deny (setq mcp-server-security-allowed-dangerous-functions '(buffer-string point)) (setq mcp-server-security-allowed-sensitive-files nil) ; No sensitive files allowed
View Security Activity:
M-x mcp-server-security-show-audit-log ; View all security events M-x mcp-server-security-show-permissions ; View cached permission decisions M-x mcp-server-security-clear-permissions ; Reset all cached permissions
Security Events Include:
Operations requiring explicit permission include file system operations (delete-file, write-region), process execution (shell-command, call-process), system functions (kill-emacs, server-start), and access to sensitive files or buffers.
Server control: M-x mcp-server-start-unix (start), M-x mcp-server-stop (stop), M-x mcp-server-restart (restart), M-x mcp-server-status (show status)
Debugging and monitoring: M-x mcp-server-toggle-debug (toggle debug logging), M-x mcp-server-list-clients (show connected clients), M-x mcp-server-get-socket-path (show socket path)
Security management: M-x mcp-server-security-show-audit-log (view security log), M-x mcp-server-security-show-permissions (view cached permissions)
Using shell wrapper (recommended):
{ "mcpServers": { "emacs": { "command": "/path/to/mcp-wrapper.sh", "args": ["$HOME/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock"], "transport": "stdio" } } }
Using Python wrapper:
{ "mcpServers": { "emacs": { "command": "python3", "args": ["/path/to/mcp-wrapper.py", "$HOME/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock"], "transport": "stdio" } } }
Direct socat (simple but less robust):
{ "mcpServers": { "emacs": { "command": "socat", "args": ["-", "UNIX-CONNECT:$HOME/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock"], "transport": "stdio" } } }
Shell wrapper (mcp-wrapper.sh) - Lightweight, uses socat, good for simple integrations:
./mcp-wrapper.sh ~/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock ./mcp-wrapper.sh /custom/path/emacs-mcp-server-myinstance.sock EMACS_MCP_DEBUG=1 ./mcp-wrapper.sh ~/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock
Python wrapper (mcp-wrapper.py) - More robust error handling, better cross-platform support:
./mcp-wrapper.py ~/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock ./mcp-wrapper.py --list-sockets EMACS_MCP_DEBUG=1 ./mcp-wrapper.py ~/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock
Environment variables for both wrappers:
EMACS_MCP_TIMEOUT: Connection timeout in seconds (default: 10)EMACS_MCP_DEBUG: Enable debug loggingFor your own MCP client implementation:
import socket import json # Connect to Emacs MCP Server sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_UNIX, socket.SOCK_STREAM) sock.connect("~/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock") # Send initialization init_msg = { "jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 1, "method": "initialize", "params": { "protocolVersion": "draft", "capabilities": {}, "clientInfo": {"name": "my-client", "version": "1.0.0"} } } sock.send((json.dumps(init_msg) + "\n").encode()) response = sock.recv(4096).decode() print(response)
Quick test: Run ./test/scripts/test-runner.sh or test a specific socket with ./test/integration/test-unix-socket-fixed.sh ~/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sock
Adding custom tools:
(mcp-server-tools-register "my-tool" "My Custom Tool" "Description of what this tool does" '((type . "object") (properties . ((param . ((type . "string"))))) (required . ["param"])) (lambda (args) (let ((param (alist-get 'param args))) (format "Result: %s" param))))
Server won't start: Check if socket directory exists and is writable, verify no other server is using the same socket path, check Emacs Messages buffer for error details.
Socket not found:
M-x mcp-server-statusM-x mcp-server-get-socket-path./mcp-wrapper.sh --list-socketsConnection refused:
ls -la ~/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server*.sockecho '{"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"method":"tools/list"}' | socat - UNIX-CONNECT:~/.emacs.d/.local/cache/emacs-mcp-server.sockMCP client issues:
Permission errors: View audit log with M-x mcp-server-security-show-audit-log, grant specific permissions with (mcp-server-security-grant-permission 'function-name), or disable prompting with (mcp-server-security-set-prompting nil).
Debug mode: Enable with (setq mcp-server-debug t) or toggle with M-x mcp-server-toggle-debug.
Multiple Emacs instances:
;; Instance 1 (setq mcp-server-socket-name "instance-1") (mcp-server-start-unix) ;; Instance 2 (setq mcp-server-socket-name "instance-2") (mcp-server-start-unix)
Dynamic socket naming:
(setq mcp-server-socket-name (lambda () (format "emacs-%s-%d" (system-name) (emacs-pid))))
Performance tips:
M-x mcp-server-list-clientsThe server uses a modular design with a transport layer (Unix domain sockets, TCP planned), protocol layer (JSON-RPC 2.0 message handling), tool registry (Elisp functions exposed as MCP tools), and security layer (permission management and validation).
┌─────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ LLM Client │────│ Unix Socket │────│ Emacs MCP │
│ (Claude/Python) │ │ Transport │ │ Server │
└─────────────────┘ └──────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
│
┌──────────────────┐
│ MCP Tools │
│ (Elisp Funcs) │
└──────────────────┘
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.