ComfyUI
STDIOIntegration server connecting ComfyUI with MCP for AI image generation workflows
Integration server connecting ComfyUI with MCP for AI image generation workflows
python src/test_comfyui.py
mcp dev src/server.py
Edit src/.env to set ComfyUI host and port:
COMFYUI_HOST=localhost COMFYUI_PORT=8188
workflows directory and declare them as new tools in the system.text_to_image
download_image tool, ordownload_image
text_to_image) using the image URL.run_workflow_with_file
Run a workflow by providing the path to a workflow JSON file.
# You should ask to agent like this.
Run comfyui workflow with text_to_image.json
example image of CursorAI
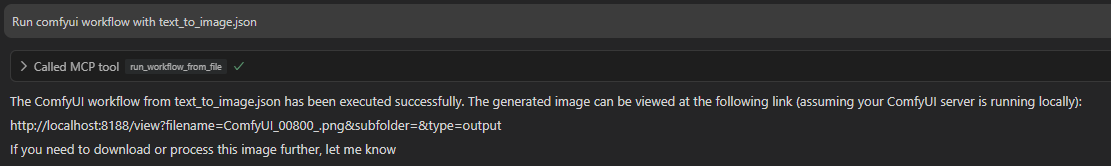
run_workflow_with_json
Run a workflow by providing the workflow JSON data directly.
# You should ask to agent like this.
Run comfyui workflow with this
{
"3": {
"inputs": {
"seed": 156680208700286,
"steps": 20,
... (workflow JSON example)
}
Example mcp.json:
{ "mcpServers": { "comfyui": { "command": "uv", "args": [ "--directory", "PATH/MCP/comfyui", "run", "--with", "mcp", "--with", "websocket-client", "--with", "python-dotenv", "mcp", "run", "src/server.py:mcp" ] } } }
download_image may be difficult since the Docker container does not share the host filesystem.RETURN_URL=false in .env to receive image data as bytes.COMFYUI_HOST in .env to the appropriate address (e.g., host.docker.internal or your server's IP).# First build image docker image build -t mcp/comfyui .
{ "mcpServers": { "comfyui": { "command": "docker", "args": [ "run", "-i", "--rm", "-p", "3001:3000", "mcp/comfyui" ] } } }
Also you can use prebuilt image.
{ "mcpServers": { "comfyui": { "command": "docker", "args": [ "run", "-i", "--rm", "-p", "3001:3000", "overseer66/mcp-comfyui" ] } } }
Run the SSE server with Docker:
docker run -i --rm -p 8001:8000 overseer66/mcp-comfyui-sse
Configure mcp.json (change localhost to your IP or domain if needed):
{ "mcpServers": { "comfyui": { "url": "http://localhost:8001/sse" } } }
NOTE: When adding new workflows as tools, you need to rebuild and redeploy the Docker images to make them available.