Authenticated Remote
HTTP-SSEAuthenticated MCP server with Entra ID protection and Graph API integration
Authenticated MCP server with Entra ID protection and Graph API integration
This sample shows how to deploy an Entra ID-protected MCP server on Azure.
The sample also uses an authorization pattern where the client acquires a token for the MCP server first, and then uses on-behalf-of flow to exchange it for a token that can be used with Microsoft Graph. It does all this in an entirely secretless manner too.
[!IMPORTANT] This is an experimental implementation and should NOT be used in production scenarios.
This sample demonstrates how to build a protected MCP server with Entra ID by implementing OAuth 2.0 Dynamic Client Registration and PKCE flow patterns that work around current gaps in Entra ID's native support for these standards. While it showcases the technical possibilities, it's intended for educational and proof-of-concept purposes only.
For production scenarios, consider using established authentication patterns with pre-registered applications and standard OAuth flows.
[!NOTE] You can use the Model Context Protocol Inspector or Visual Studio Code to test this MCP server.
This implementation uses a sophisticated OAuth 2.0 flow with PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange) to securely authenticate MCP clients. Here's how it all fits together:
sequenceDiagram participant Client as MCP Client participant Browser as User's Browser participant APIM as API Management participant Entra as Entra ID participant Function as Azure Function participant Graph as Microsoft Graph Note over Client,Graph: 1. Discovery & Registration Client->>APIM: GET /.well-known/oauth-authorization-server APIM->>Client: OAuth metadata (authorization_endpoint, token_endpoint, etc.) Client->>APIM: POST /register (Dynamic Client Registration) Note over APIM: Store client info in CosmosDB<br/>Generate unique client_id APIM->>Client: Client credentials (client_id, no secret) Note over Client,Graph: 2. Authorization with PKCE Note over Client: Generate code_verifier & code_challenge Client->>Browser: Open authorization URL with PKCE params Browser->>APIM: GET /authorize?client_id=...&code_challenge=... Note over APIM: Check for existing consent cookie<br/>🍪 __Host-MCP_APPROVED_CLIENTS alt No previous consent APIM->>Browser: Redirect to /consent page Note over Browser: User reviews permissions and clicks "Allow" Browser->>APIM: POST /consent (with CSRF protection) Note over APIM: Set consent cookie<br/>🍪 __Host-MCP_APPROVED_CLIENTS<br/>🍪 __Host-MCP_CONSENT_STATE end APIM->>Browser: Redirect to Entra ID with state correlation Note over APIM: Set Entra state cookie<br/>🍪 __Host-MCP_ENTRA_STATE<br/>(contains sessionId|entraidState|clientState) Browser->>Entra: Authorize with Entra ID Note over Browser: User authenticates with Entra ID Entra->>APIM: Callback with authorization code Note over APIM: Validate state correlation<br/>Exchange code for Entra access token<br/>Generate encrypted session token APIM->>Browser: Redirect with MCP authorization code Note over Client,Graph: 3. Token Exchange Browser->>APIM: POST /token (code + code_verifier) Note over APIM: Validate PKCE challenge<br/>Return encrypted session token APIM->>Browser: Access token (encrypted session key) Browser->>Client: Token for MCP communication Note over Client,Graph: 4. Authenticated MCP Communication Client->>APIM: GET /mcp/sse (with Bearer token) Note over APIM: Decrypt session token<br/>Lookup cached Entra token<br/>Add to request for downstream APIM->>Function: Forward with Entra access token Function->>Graph: API calls using on-behalf-of flow Graph->>Function: User data Function->>APIM: MCP response APIM->>Client: Authenticated MCP response
This implementation uses several security mechanisms and cookies to ensure a secure flow:
| Cookie | Purpose |
|---|---|
__Host-MCP_APPROVED_CLIENTS | Remembers user consent for specific clients |
__Host-MCP_DENIED_CLIENTS | Remembers denied consent to prevent re-prompting |
__Host-MCP_CONSENT_STATE | Validates consent form submissions |
__Host-MCP_ENTRA_STATE | Correlates Entra ID callback with original request |
__Host-MCP_CSRF_TOKEN | Protects against CSRF attacks on consent forms |
[!NOTE] All cookies use
__Host-prefix, Secure, HttpOnly, and SameSite=Lax for maximum security (except__Host-MCP_ENTRA_STATEwhich uses SameSite=None for cross-site redirects).
Key Security Features:
__Host- prefix for maximum securityFollow these steps to get started.
Clone the repository locally:
git clone https://github.com/localden/remote-auth-mcp-apim-py
Navigate to the repository in your terminal:
cd remote-auth-mcp-apim-py
Ensure the Microsoft.App resource provider is registered on your subscription either on the Azure portal or by running the following Azure CLI command:
az login az provider register --namespace Microsoft.App --wait
Log in to Azure Developer CLI:
azd auth login
Deploy the project to Azure:
azd up
[!IMPORTANT] Deploying this project will incur Azure cost. If you are deploying for testing and experimentation, make sure to delete the created resource group after testing.
When you run azd up, resources declared in the infra directory will be provisioned in your Azure account. You can go through the existing Bicep files to see what infrastructure will be automatically deployed.
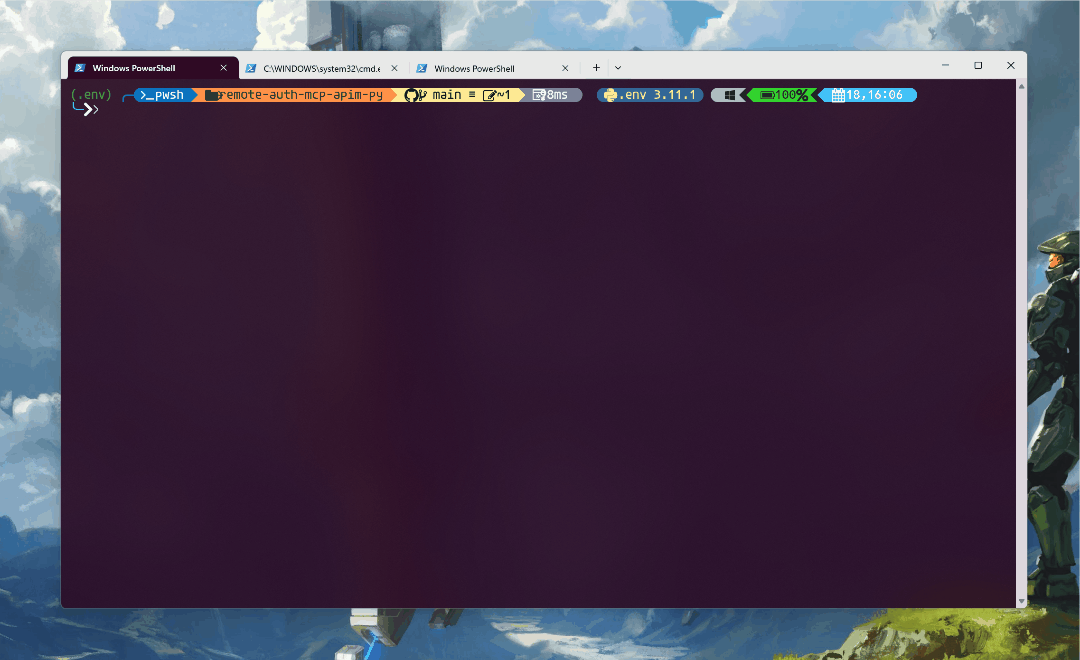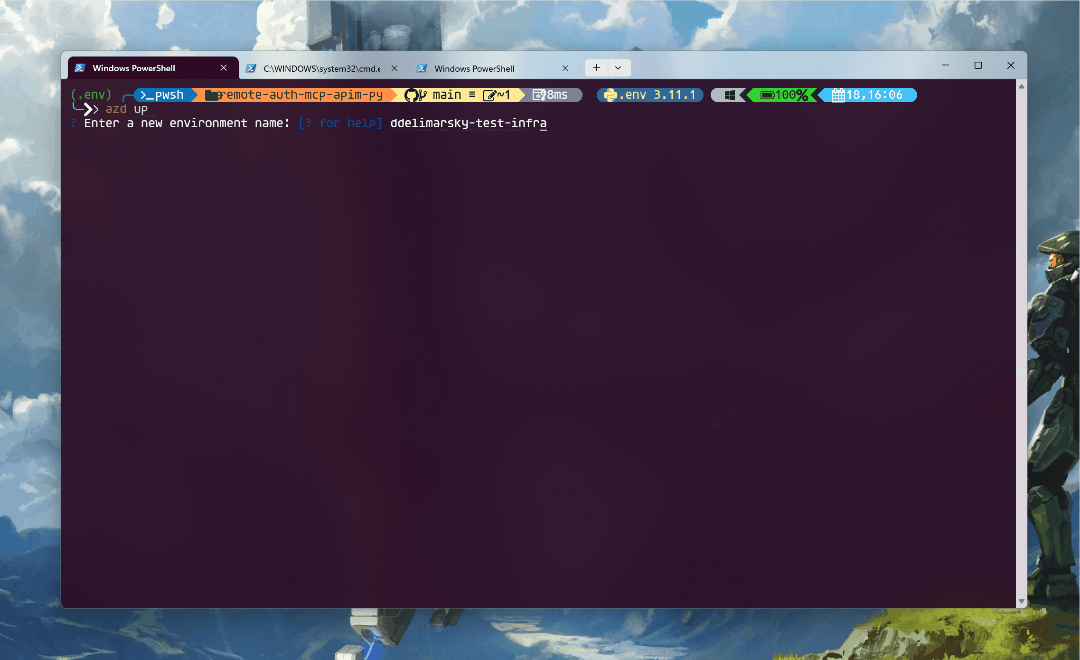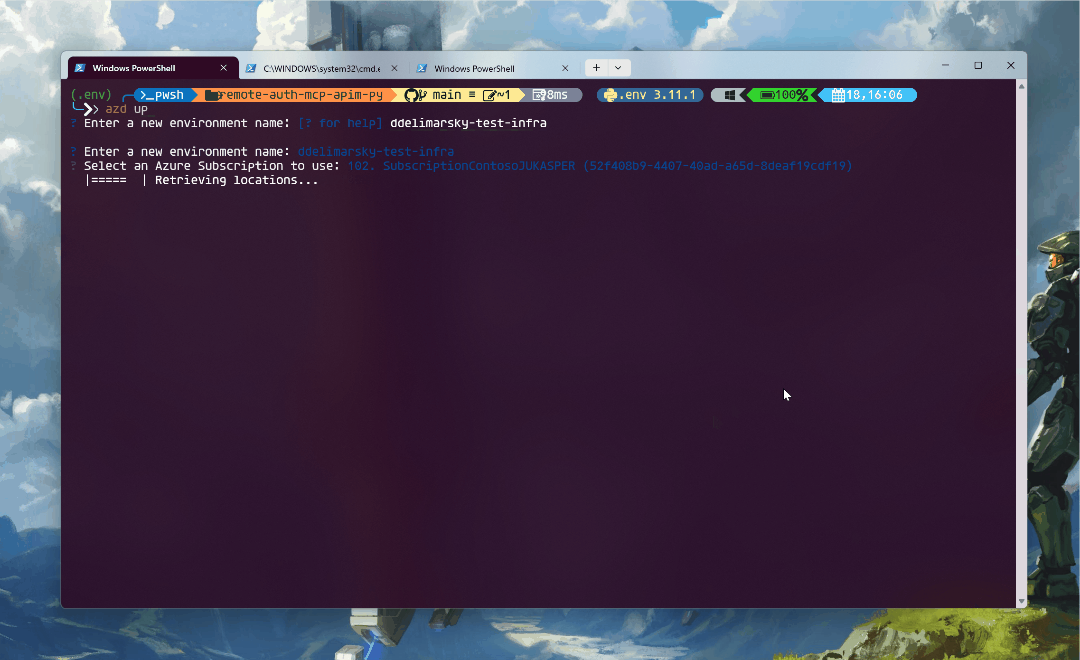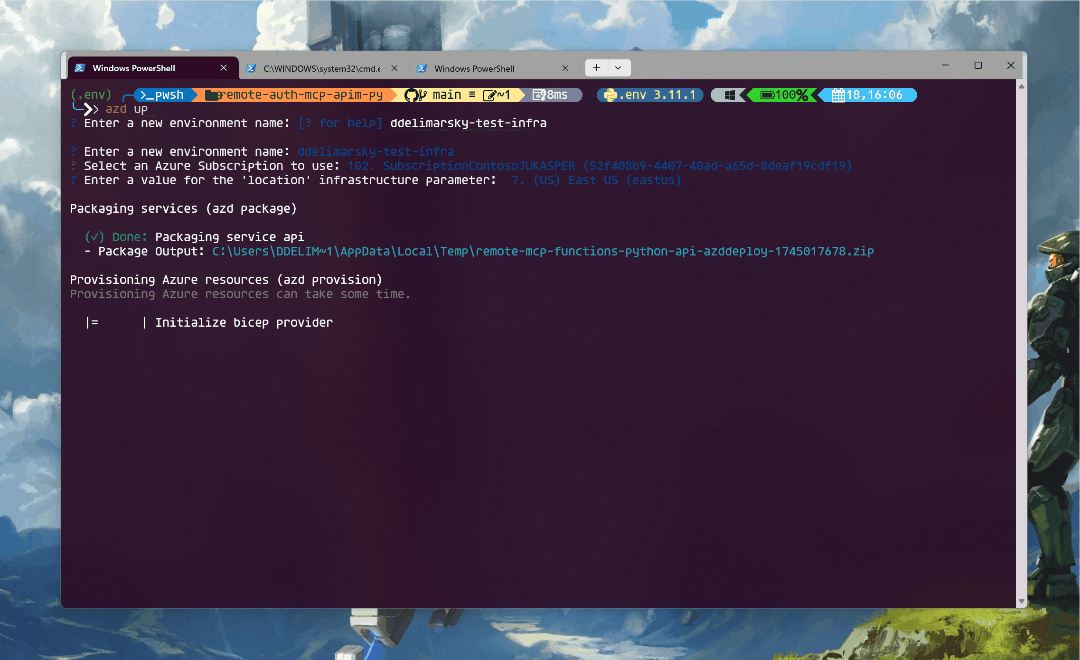
Once the deployment completes, you will be see the endpoint printed in the terminal:
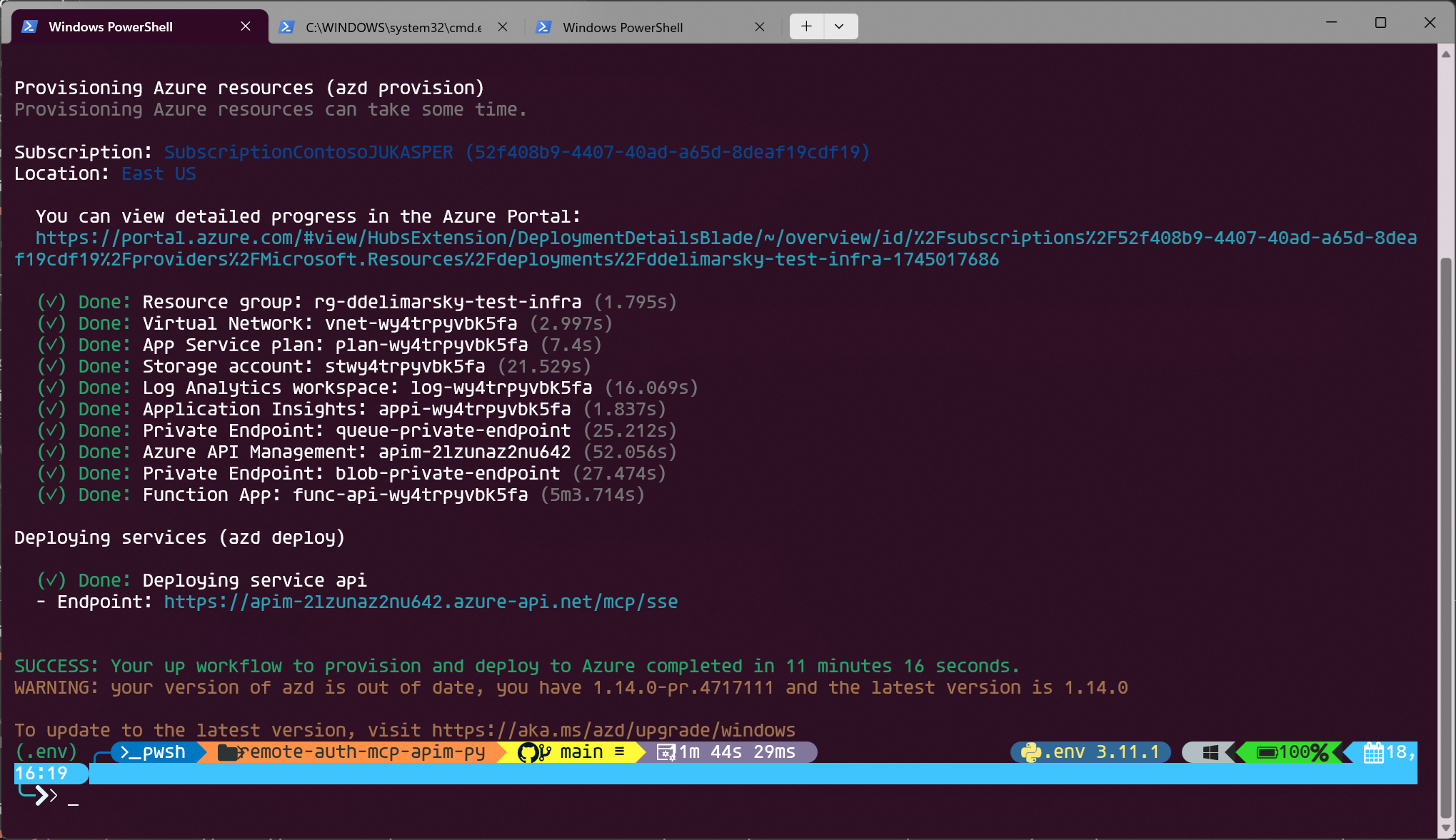
For example, in the screenshot above the endpoint is https://apim-2lzunaz2nu642.azure-api.net/mcp/sse. Copy it.
[!NOTE] Prior to the next step, make sure that you have Node.js installed - it's required to run the Model Context Protocol Inspector.
In your terminal, run:
npx @modelcontextprotocol/[email protected]
[!NOTE] We're using the
0.9.0release of the Model Context Protocol Inspector because it's the most stable version when it comes to testing protected MCP servers.
This will give an endpoint where you can see Model Context Protocol Inspector running locally. Open the URL in your browser.
Switch the Transport Type to SSE and set the URL to the endpoint that you got from running the deployment. Click Connect.
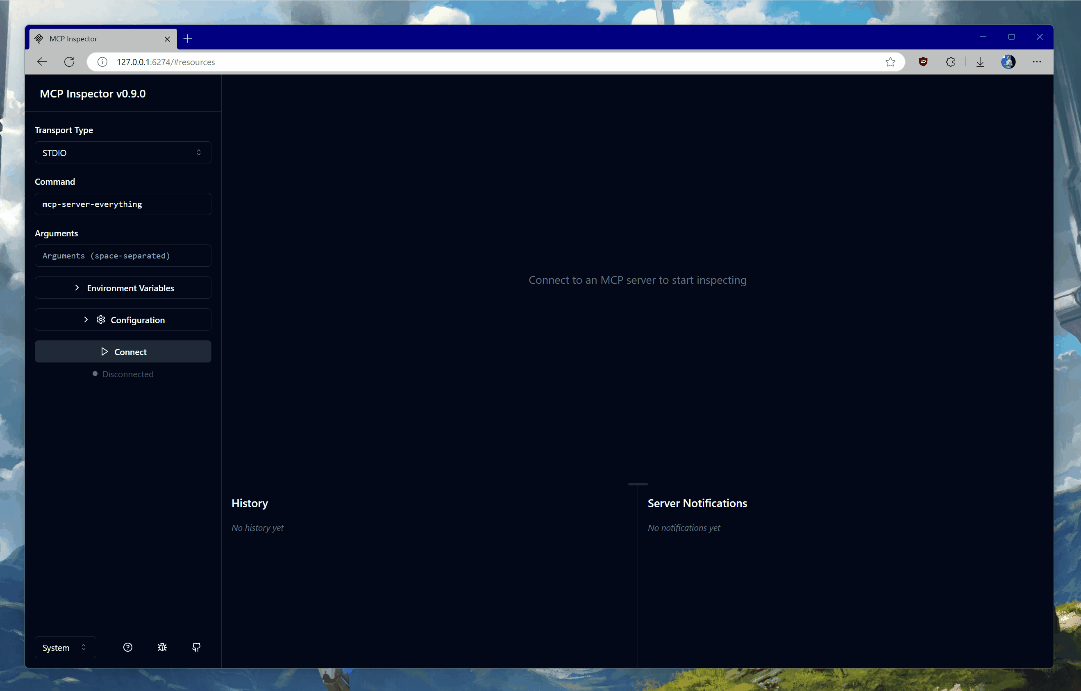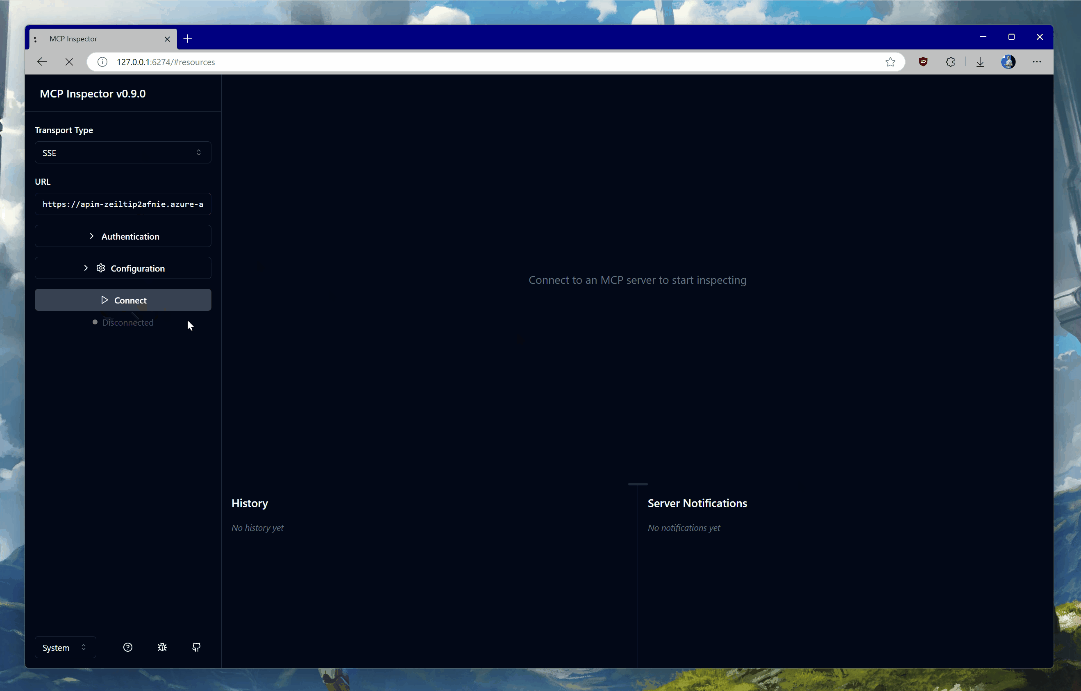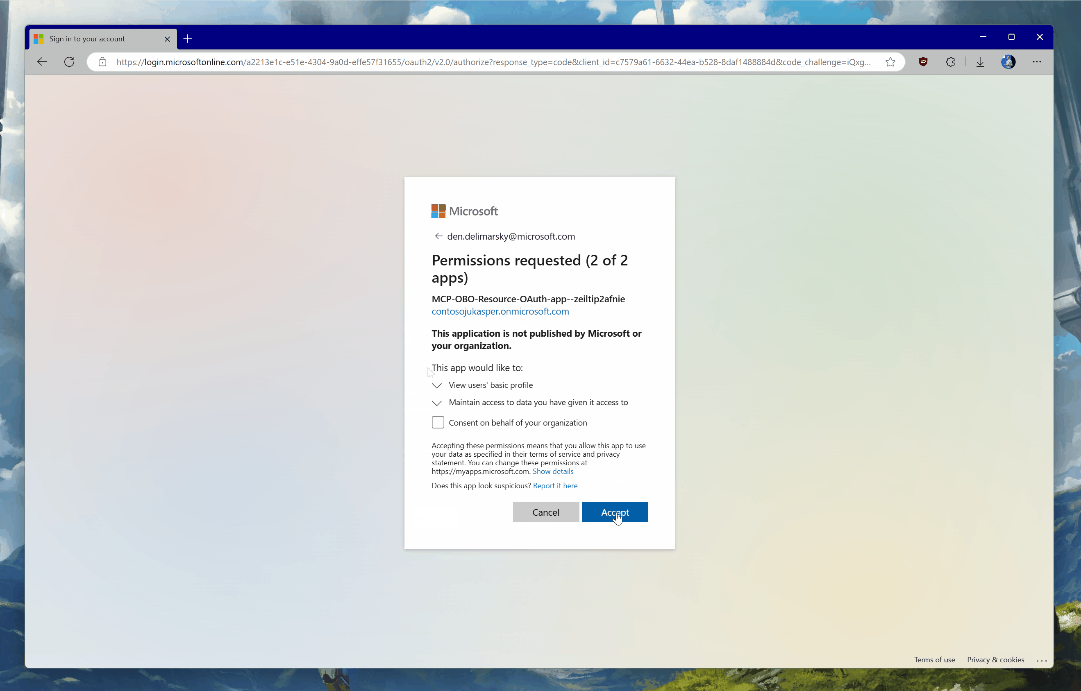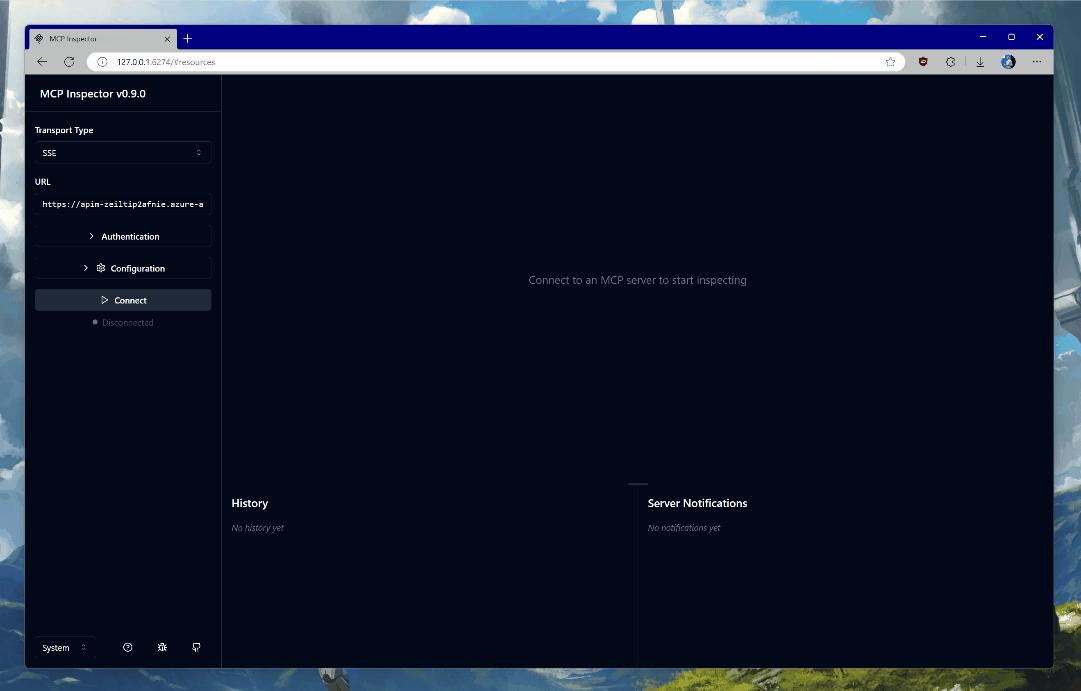
You will be prompted to authenticate with the credentials in the tenant in which you deployed the infrastructure. The Entra ID applications are dynamically registered at deployment time - one for the server, and another that will be used for on-behalf-of flow to acquire Microsoft Graph access.
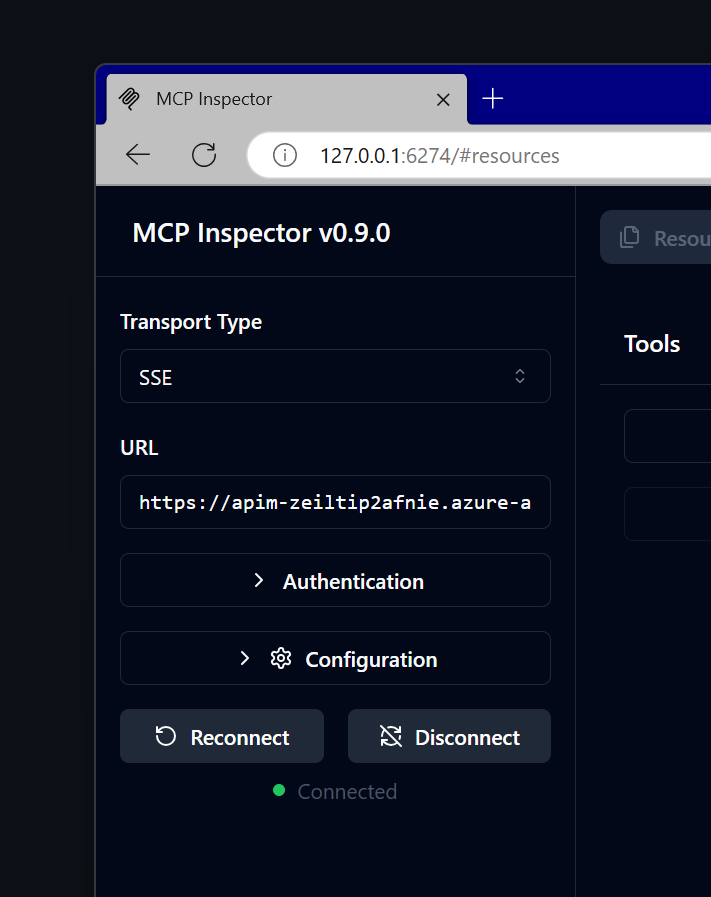
Once you consent, you will be returned back to the Model Context Protocol Inspector landing page. Wait a few seconds until the connection is established - you will see a green Connected label on the page.
Once connected, click on List Tools and select get_graph_user_details. This will enable you to get data about the currently authenticated user from Microsoft Graph. Click Run Tool.
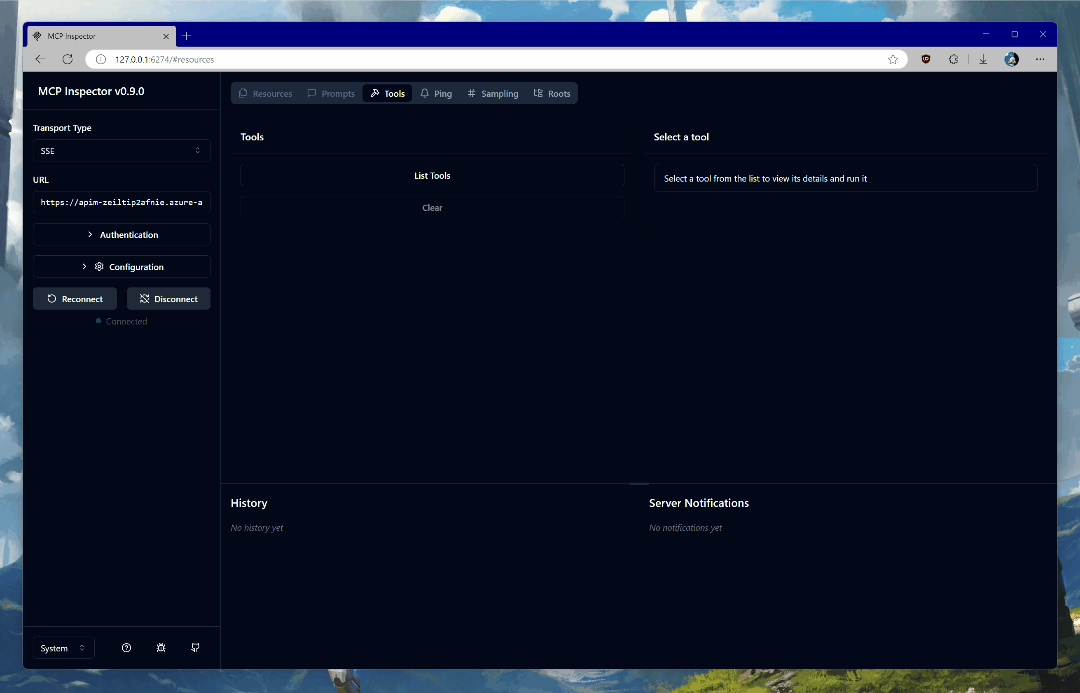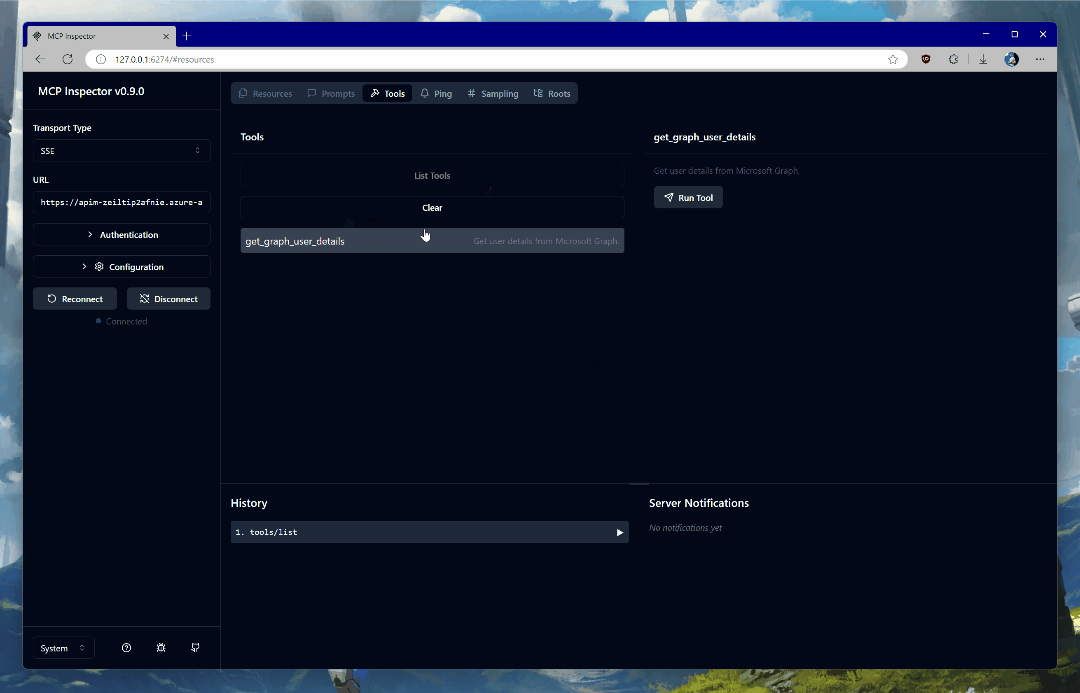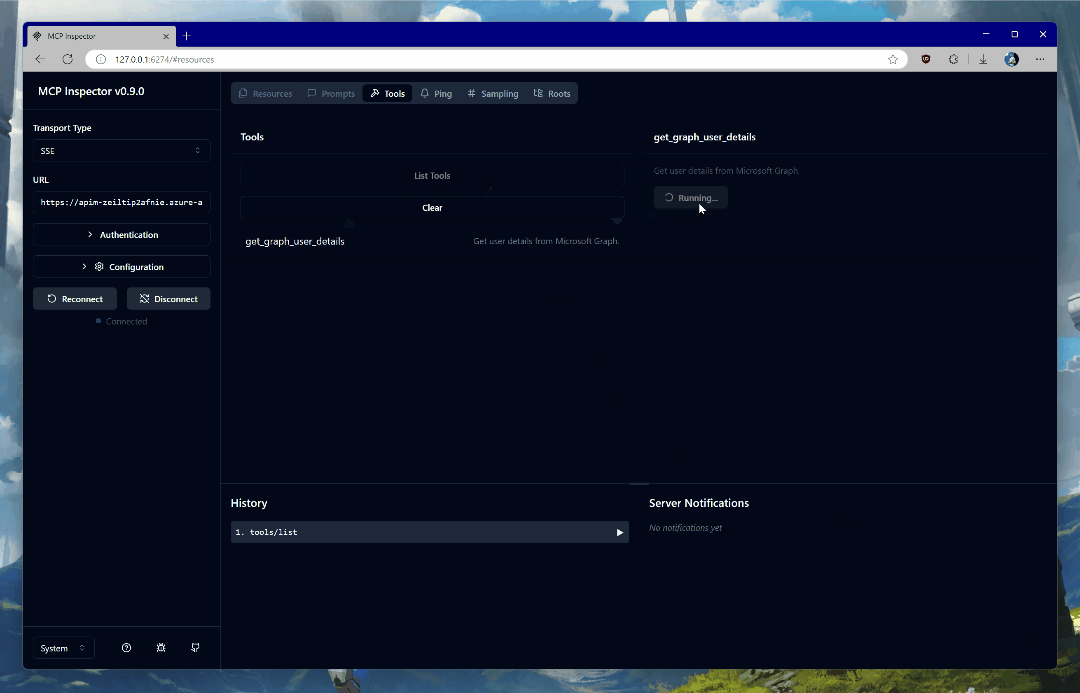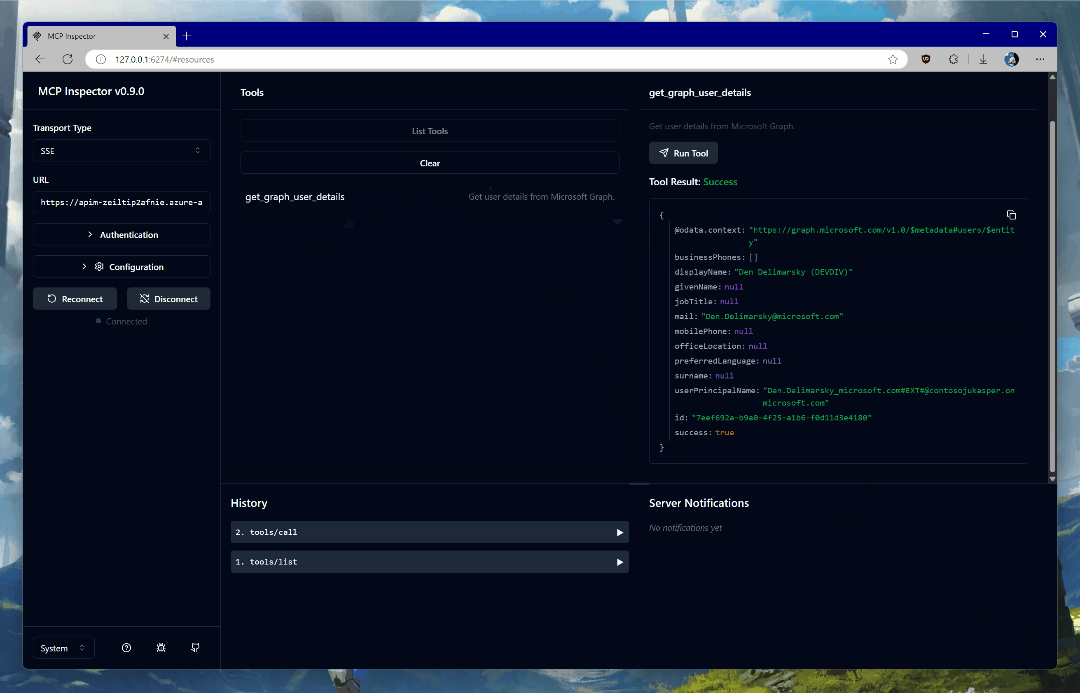
If all goes well, you will see your user data in the response block, like this:
{ "@odata.context": "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/$metadata#users/$entity", "businessPhones": [], "displayName": "YOUR_NAME", "givenName": null, "jobTitle": null, "mail": "YOUR_EMAIL", "mobilePhone": null, "officeLocation": null, "preferredLanguage": null, "surname": null, "userPrincipalName": "YOUR_UPN", "id": "c6b77314-c0ec-44b2-b0bb-2c971a753f0c", "success": true }
Make sure to open an issue if you encounter any roadblocks or have comments.